Abstract
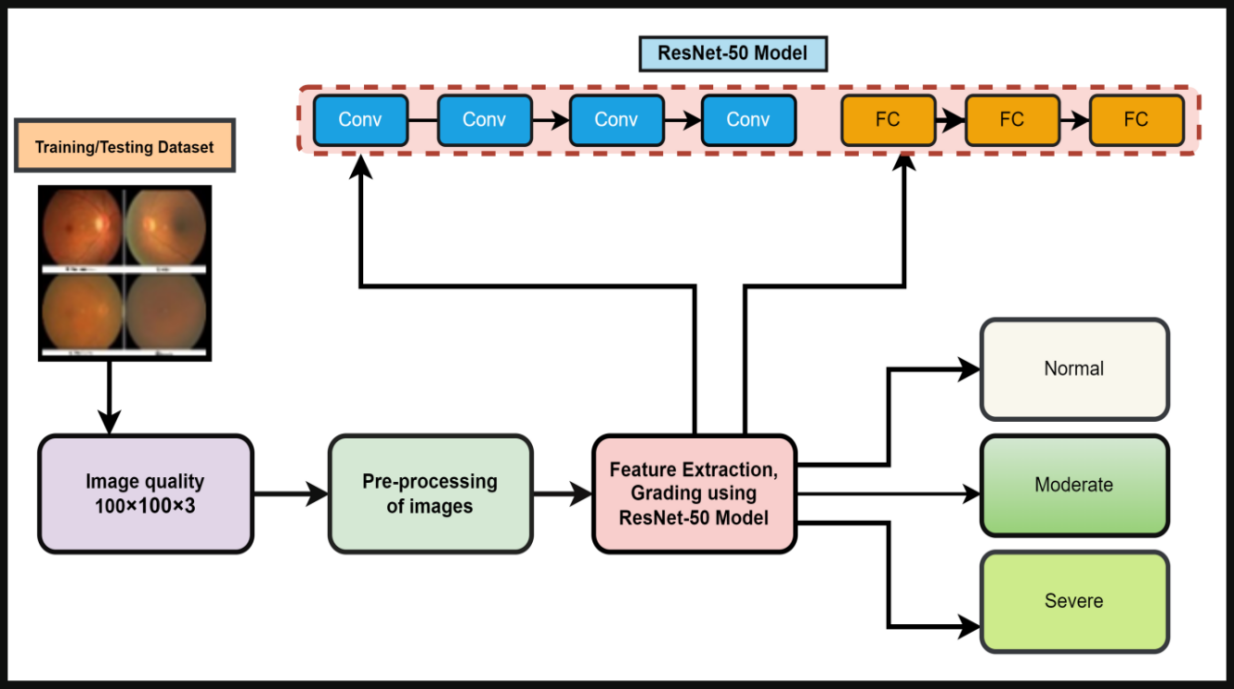
Cataracts are a leading cause of blindness in Pakistan, contributing to more than 54% of cases due to poor living condition, nutritional deficiencies, and limited healthcare access. Early detection is critical to avoid invasive treatments,but current diagnostic approaches often identify cataracts at advanced stages. This paper presents an advanced,automated cataract detection system using deep learning specifically the ResNet-50 architecture, to address this gap. The model processes fundus retinal images curated from diverse datasets, classified by ophthalmologic experts through a rigorous three-stage process. By leveraging the ResNet-50 model, cataracts are categorized into normal,moderate,and severe, achieving an accuracy of 97.56% on full images. Notably, the system performs well even on partial images with 70% visibility, maintaining an accuracy of 95.23%, thus minimizing the need for extensive images restoration. The dataset was augmented to include 17,500 images,ensuring robust training. The model's ability to detect cataracts with high precision in images with varying visibility(70% ,80%,85% and beyond) demonstrate its flexibility and reliability, consistently achieving accuracy above 95.50%. This research offers a non-invasive, efficient solution particularly suited for remote areas, addressing the limitations of the late-stage diagnoses. It represent a significant advancement in cataract detection and has the potential to revolutionize global cataracts identification through early, accurate intervention.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Khan, I., Akbar, W., Soomro, A., Hussain, T., Khalil, I., Khan, M. N., & Salam, A. (2024). Enhancing Ocular Health Precision: Cataract Detection Using Fundus Images and ResNet-50. IECE Transactions on Intelligent Systematics, 1(3), 145-160. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIS.2024.640345
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue