Abstract
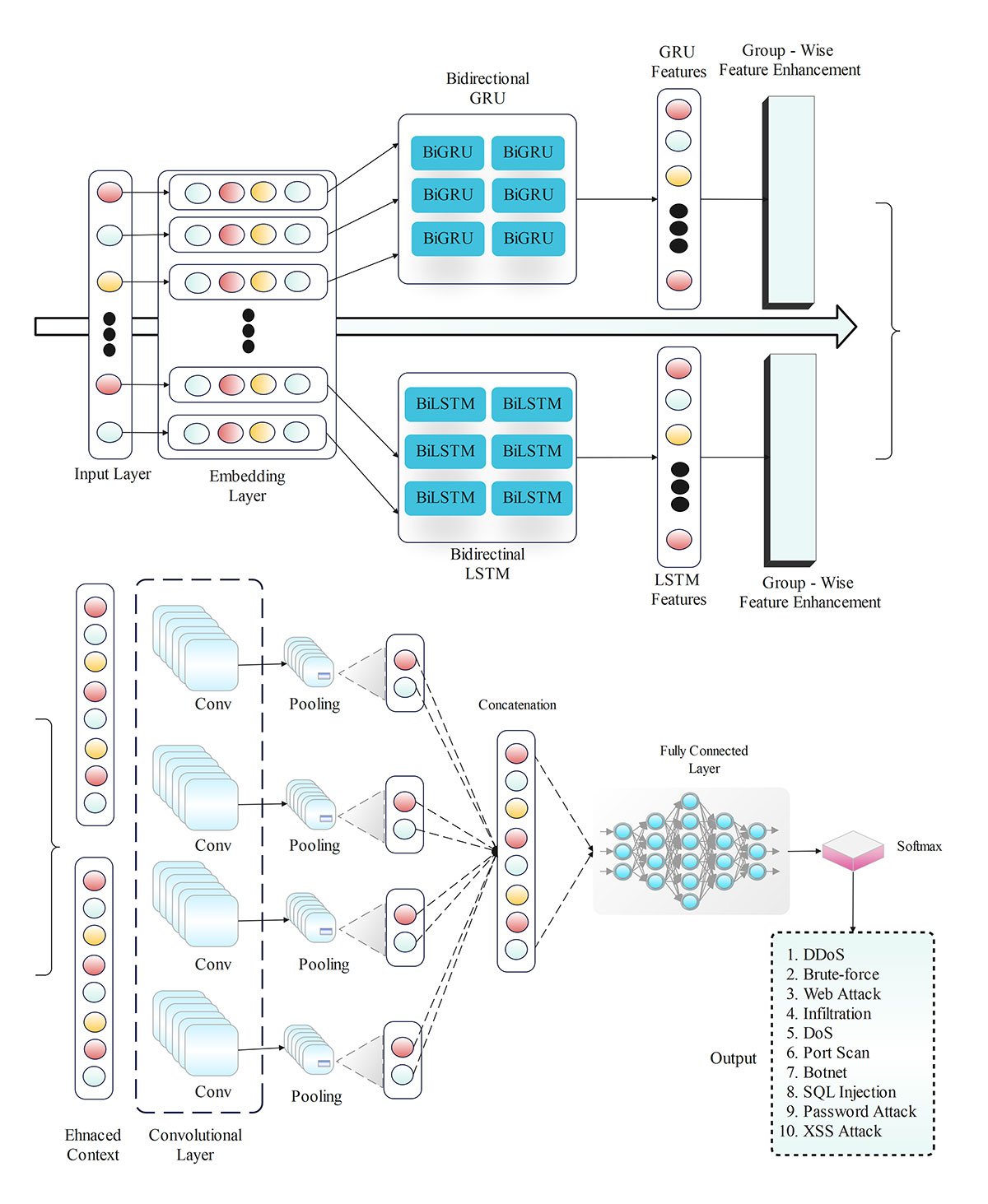
To address evolving security challenges in cloud computing, this study proposes a hybrid deep learning architecture integrating Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Units (BiGRU) for cloud intrusion detection. The BiLSTM-BiGRU model synergizes BiLSTM's long-term dependency modeling with BiGRU's efficient gating mechanisms, achieving a detection accuracy of 96.7% on the CIC-IDS 2018 dataset. It outperforms CNN-LSTM baselines by 2.2% accuracy, 3.3% precision, 3.6% recall, and 3.6% F1-score while maintaining 0.03% false positive rate. The architecture demonstrates operational efficiency through 20% reduced computational latency and 15% lower memory footprint compared to conventional models, enabled by residual memory preservation and parallel processing capabilities. Experimental results validate its dual competence in detecting both known attack patterns (98.1% recognition rate) and zero-day threats (93.4% anomaly identification), establishing a methodological framework for real-time cloud security services. This work advances hybrid deep learning applications in trusted computing environments through optimized temporal feature extraction and resource-aware threat detection.
Keywords
cloud security
network intrusion detection
deep learning
BiLSTM-BiGRU
hybrid models
cybersecurity
cloud computing
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Haider, Z. A., Zeb, A., Rahman, T., Khan, F. M., Khan, I. U., Sohail, Q., Bilal, H., Khan, M. A., & Ullah, I. (2025). Optimizing Cloud Security with a Hybrid BiLSTM-BiGRU Model for Efficient Intrusion Detection. IECE Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control, 2(2), 106–121. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSCC.2024.433246
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue